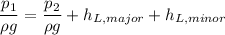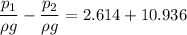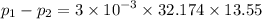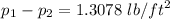Solution:
The velocity of the exhaust air flow using continuity equation
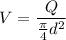
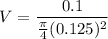
= 8.148 ft/s
Reynolds number,
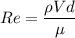
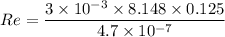
= 6501.06
As Re > 4000, the flow is turbulent.
Now calculating the friction factor of the flow,
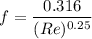
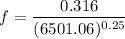
= 0.03519
Calculating the major head loss in the pipe
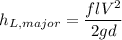
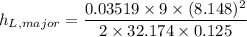
= 2.614 ft
Calculating the minor head loss in the pipe
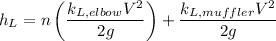
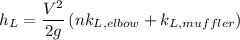
Here, n = number of elbows.
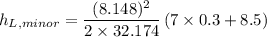
= 10.936 ft
Now using Bernoulli equation between the entrance of the pipe and the exit of the pipe
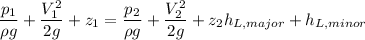
Substitute
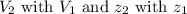 , we get
, we get