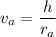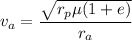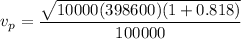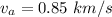Solution :
Given :
radius of perigee,
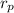 = 10,000 km
= 10,000 km
radius of apogee,
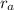 = 100,000 km
= 100,000 km
a). Eccentricity of the orbit
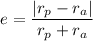
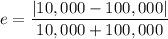
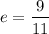
or e = 0.818
b). Semi major axis of the orbit
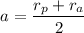
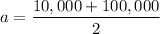
= 55,000 km
c). period of orbit
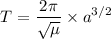
Replacing μ with
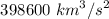
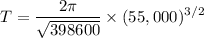
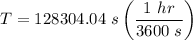
T = 35.64 hr
d). Specific energy of the orbit
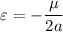
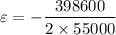
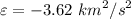
e). the equation of the distance to the focus
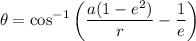
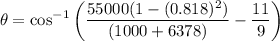
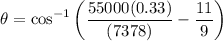
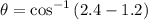
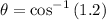
θ = 1.002°
f).Calculating the angular momentum
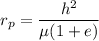
or
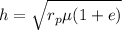
Now calculate the radial velocity
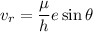
Substituting for h,
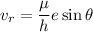
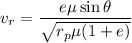
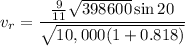
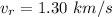
Now calculating the azimuthal velocity
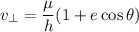
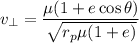
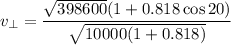
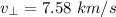
g). Velocity at perigee
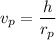
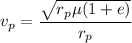
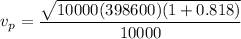
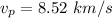
Now calculate the velocity of the apogee