Answer:
See the explanion below
Step-by-step explanation:
Linear momentum is defined as the product of mass by velocity and can be calculated by the following equation.
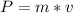
where:
P = momentum [kg*m/s]
m = mass [kg]
v = velocity [m/s]
When the ball hits the wall it receives a force for a very short time, this time and force value is known as momentum and can be calculated by the following expression.
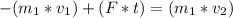
where:
m₁ = mass of the ball [kg]
v₁ = 5 [m/s]
v₂ = 5 [m/s]
v₁ = v₂
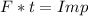
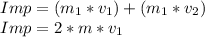
It can be said that the impulse is equal to 2 times the speed of throwing by the mass.