Answer:
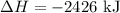
Step-by-step explanation:
To find the enthalpy change of the target reaction, we can use Hess's Law.
Reversing the third reaction yields:
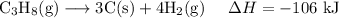
Multiplying the first reaction by three yields:
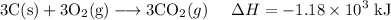
Multiplying the second reaction by four yields:
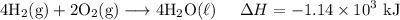
Adding all equations yield:
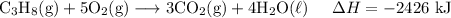
Hence, the enthalpy change of the target reaction is -2426 kJ.