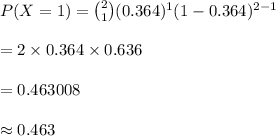Answer:
(a) 0.1325
(b) 0.4045
(c) 0.463
Explanation:
Let X denote the number of defective transistors.
The proportion of defective transistors is, p = 4/11 = 0.364.
All the transistors are independent of the others.
The random variable X follows a binomial distribution.
(a)
Compute the probability that both transistors are defective, if 2 transistors are drawn from the box together as follows:

(b)
Compute the probability that neither transistors are defective, if 2 transistors are drawn from the box together as follows:

(c)
Compute the probability that one transistors are defective, if 2 transistors are drawn from the box together as follows: