Answer:
0.387 g
Step-by-step explanation:
pH of the buffer = 1
V = Volume of solution = 100 mL
[HA] = Molarity of HA = 0.1 M
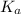 = Acid dissociation constant =
= Acid dissociation constant =
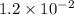
(assuming base as
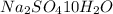 )
)
Molar mass of base = 322.2 g/mol
pKa is given by
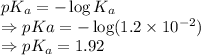
From the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation we get
![pH=pK_a+\log([A^-])/([HA])\\\Rightarrow pH-pK_a=\log([A^-])/([HA])\\\Rightarrow 10^(pH-pK_a)=([A^-])/([HA])\\\Rightarrow [A^-]=10^(pH-pK_a)[HA]\\\Rightarrow [A^-]=10^(1-1.92)*0.1\\\Rightarrow [A^-]=0.01202\ \text{M}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/soa3rohckpbnidokir23f0f0ir9k5vn75b.png)
Moles of base
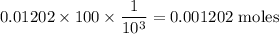
Mass of base is given by
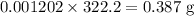
The required mass of the base is 0.387 g.