Answer:
See below for all information
Explanation:
Given Information
- Observed Sample Proportion:
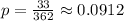
- Hypothesized Population Proportion:
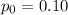
- Sample Size:
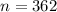
- Significance Level:
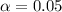
- We should conduct a two-tailed one-proportion z-test (remember to double the p-value to consider both tails!)
- Assume conditions are met
Null and Alternate Hypotheses
- Null:
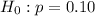 (this tells us that the actual proportion of inaccurate orders of 10% is equal to the observed proportion of inaccurate orders)
(this tells us that the actual proportion of inaccurate orders of 10% is equal to the observed proportion of inaccurate orders) - Alternate:
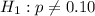 (this tells us that the actual proportion of inaccurate orders of 10% is NOT equal to the observed proportion of inaccurate orders)
(this tells us that the actual proportion of inaccurate orders of 10% is NOT equal to the observed proportion of inaccurate orders)
Determine z-statistic
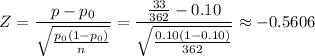
Determine p-value from z-statistic
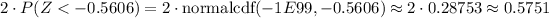
Draw conclusion of p-value based on given significance level
Since
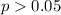 , we fail to reject the null hypothesis. This means that we do have sufficient evidence to say that the observed rate of inaccurate orders is equal to 10%, making it extremely likely that the null hypothesis is true.
, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. This means that we do have sufficient evidence to say that the observed rate of inaccurate orders is equal to 10%, making it extremely likely that the null hypothesis is true.