Answer:
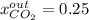
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello.
In this case, for the reactive scheme, it is very convenient to write each species' mole balance as shown below:
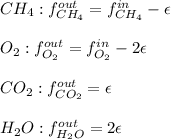
Whereas
 accounts for the reaction extent. However, as all the methane is consumed, from the methane balance:
accounts for the reaction extent. However, as all the methane is consumed, from the methane balance:
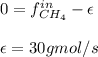
Thus, we can compute the rest of the outlet mole flows since not all the oxygen is consumed as it is in excess:
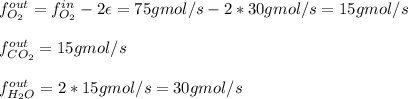
It means that the mole fraction of carbon dioxide in that output is:
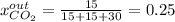
Best regards.