Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
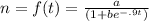
At t = 0
30 =
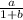
30 + 30 b = a
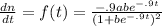
For t = o
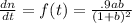
given
24 =
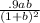
24 =
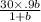
24 = 27b / 1 + b
24 + 24 b = 27 b
24 = 3 b
b = 8
a = 30 + 30 x 8 = 270
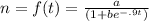
Put t = infinity
n = a = 270
So at infinite time yeast population will stabilise at number 270 .