Answer:
(a) The area of the duct exit is 1.67 m²
(b) The air pressure at the exit is 1.195 x 10⁵ N/m²
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
inlet area, A₁ = 5 m²
inlet velocity, V₁ = 10 m/s
exit velocity, V₂ = 30 m/s
(a) The area of the duct exit is determined by applying continuity equation;
A₁V₁ = A₂V₂
Where;
A₂ is the area of the duct exit
A₂ = (A₁V₁) / (V₂)
A₂ = (5 x 10) / (30)
A₂ = 1.67 m²
(b) Apply Bernoulli’s equation to determine the pressure at the exit;
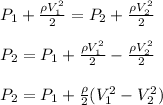
Density of air at 300k = 1.177 kg/m³
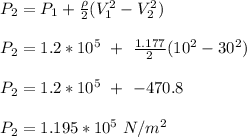
Therefore, the air pressure at the exit is 1.195 x 10⁵ N/m²