Answer:
v=6.05 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Th initial velocity of the lander, u = 1.2 m/s
The lander is at a height of 1.8 m, d = 1.8 m
We need to find the velocity of the lander at impact. It is a concept based on the conservation of mechanical energy. So,
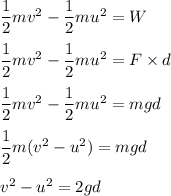
v is the velocity of the lander at the impact
g is the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Mars, which is 0.4 times that on the surface of the Earth, g = 0.4 × 9.8 = 3.92 m/s²
So,
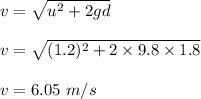
So, the velocity of the lander at the impact is 6.05 m/s.