Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that:
At state 1:
Pressure P₁ = 20 bar
Volume V₁ = 0.03
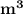
From the tables at saturated vapour;
Temperature T₁ = 212.4⁰ C ;
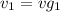 = 0.0996
= 0.0996
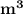 / kg
/ kg
The mass inside the cylinder is m = 0.3 kg, which is constant.
The specific internal energy u₁ = ug₁ = 2599.2 kJ/kg
At state 2:
Temperature T₂ = 200⁰ C
Since the 1 - 2 occurs in an isochoric process v₂ = v₁ = 0.099
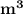 / kg
/ kg
From temperature T₂ = 200⁰ C
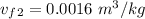
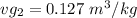
Since
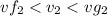 , the saturated pressure at state 2 i.e. P₂ = 15.5 bar
, the saturated pressure at state 2 i.e. P₂ = 15.5 bar
Mixture quality
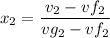
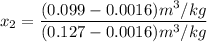
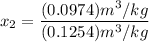
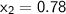
At temperature T₂, the specific internal energy
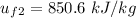 , also
, also
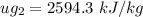
Thus,
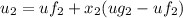
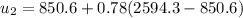
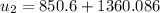
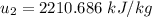
At state 3:
Temperature
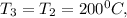
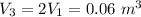
Specific volume
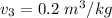
Thus;
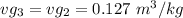 ,
,
SInce
 , therefore, the phase is in a superheated vapour state.
, therefore, the phase is in a superheated vapour state.
From the tables of superheated vapour tables; at
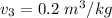 and T₃ = 200⁰ C
and T₃ = 200⁰ C
The pressure = 10 bar and v =0.206
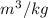
The specific internal energy
 at the pressure of 10 bar = 2622.3 kJ/kg
at the pressure of 10 bar = 2622.3 kJ/kg
The changes in the specific internal energy is:

= (2210.686 - 2599.2) kJ/kg
= -388.514 kJ/kg
≅ - 389 kJ/kg

= (2622.3 - 2210.686) kJ/kg
= 411.614 kJ/kg
≅ 410 kJ/kg
We can see the correct sketches of the T-v plot showing the diagrammatic expression in the image attached below.