Answer:
The steady rate of heat transfer through the glass window is 707.317 watts.
Step-by-step explanation:
A figure describing the problem is included below as attachment. From First Law of Thermodynamics we get that steady rate of heat transfer through the glass window is the sum of thermal conductive and convective heat rates, all measured in watts:
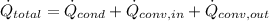 (Eq. 1)
(Eq. 1)
Given that window is represented as a flat element, we can expand (Eq. 1) as follows:
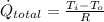 (Eq. 2)
(Eq. 2)
Where:
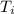 ,
,
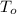 - Indoor and outdoor temperatures, measured in Celsius.
- Indoor and outdoor temperatures, measured in Celsius.
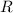 - Overall thermal resistance, measured in Celsius per watt.
- Overall thermal resistance, measured in Celsius per watt.
Now, we know that glass window is configurated in series and overall thermal resistance is:
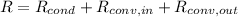 (Eq. 3)
(Eq. 3)
Where:
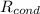 - Conductive thermal resistance, measured in Celsius per watt.
- Conductive thermal resistance, measured in Celsius per watt.
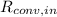 ,
,
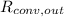 - Indoor and outdoor convective thermal resistances, measured in Celsius per watt.
- Indoor and outdoor convective thermal resistances, measured in Celsius per watt.
And we expand the expression as follows:
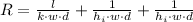
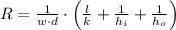 (Eq. 4)
(Eq. 4)
Where:
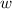 - Width of the glass window, measured in meters.
- Width of the glass window, measured in meters.
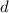 - Length of the glass window, measured in meters.
- Length of the glass window, measured in meters.
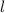 - Thickness of the glass window, measured in meters.
- Thickness of the glass window, measured in meters.
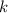 - Thermal conductivity, measured in watts per meter-Celsius.
- Thermal conductivity, measured in watts per meter-Celsius.
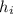 ,
,
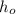 - Indoor and outdoor convection coefficients, measured in watts per square meter-Celsius.
- Indoor and outdoor convection coefficients, measured in watts per square meter-Celsius.
If we know that
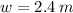 ,
,
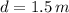 ,
,
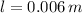 ,
,
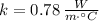 ,
,
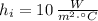 and
and
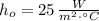 , the overall thermal resistance is:
, the overall thermal resistance is:
![R = \left[(1)/((2.4\,m)\cdot (1.5\,m))\right] \cdot \left((0.006\,m)/(0.78\,(W)/(m\cdot ^(\circ)C) )+(1)/(10\,(W)/(m^(2)\cdot ^(\circ)C) )+(1)/(25\,(W)/(m^(2)\cdot ^(\circ)C) ) \right)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/ob7zcp2go04j8oblzi9bi26m957fga5ljb.png)
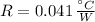
Now, we obtain the steady rate of heat transfer from (Eq. 2): (
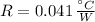 ,
,
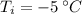 ,
,
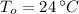 )
)
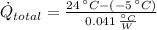
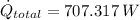
The steady rate of heat transfer through the glass window is 707.317 watts.