Answer:
The specific heat capacity of the metal is approximately 0.3903 J/(g·°C)
Step-by-step explanation:
The mass of the sample of the unknown metal,
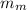 = 134.0 g
= 134.0 g
The temperature to which the metal is raised,
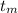 = 91.0°C
= 91.0°C
The mass of water into which the mass of metal is placed,
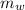 = 125 g
= 125 g
The temperature of the water into which the metal is placed,
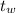 = 25.0°C
= 25.0°C
The final temperature of the water,
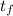 = 31.0°C
= 31.0°C
The specific heat capacity of water,
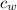 = 4.184 J/(g·°C)
= 4.184 J/(g·°C)
The specific heat capacity of the metal =
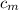
Therefore, by the first laws of thermodynamics we have;
The heat transferred = Heat supplied by the metal = Heat gained by the water
The heat transferred, ΔQ, is given as follows;
ΔQ =
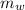 ×
×
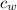 ×(
×(
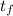 -
-
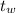 ) =
) =
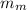 ×
×
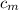 ×(
×(
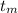 -
-
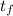 )
)
125 × 4.184 × (31 - 25) = 134 ×
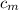 × (91 - 31)
× (91 - 31)
∴
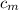 = (125 × 4.184 × (31 - 25))/(134 × (91 - 31)) ≈ 0.3903 J/(g·°C)
= (125 × 4.184 × (31 - 25))/(134 × (91 - 31)) ≈ 0.3903 J/(g·°C)
The specific heat capacity of the metal =
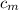 ≈ 0.3903 J/(g·°C)
≈ 0.3903 J/(g·°C)