Answer:
1)
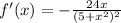
2)
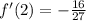
Explanation:
So we have the function:
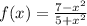
And we want to find f'(x).
To do so, we can use the quotient rule.
So, let's take the derivative of both sides:
![(d)/(dx)[f(x)]=(d)/(dx)[(7-x^2)/(5+x^2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/ha3wm6txamgxnd9ptcvwt9fvq4vhzimvwj.png)
Remember that the quotient rule is:
![(d)/(dx)[f/g]=(f'g-fg')/(g^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/j0vrn6fqgxs0e1tskact5gg0ydwxpids0u.png)
In our equation, f is (7-x^2) and g is (5+x^2).
So, using the quotient rule, our derivative f'(x) is:
-(7-x^2)(d)/(dx)[5+x^2])/((5+x^2)^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/61k4evmnzp84ovunfr195fjt1ru4dp4gpl.png)
Differentiate:
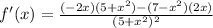
Simplify. Distribute in the numerator:
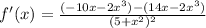
Distribute:
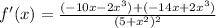
The cubed terms cancel. This leaves:
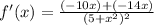
Add. So, our derivative is:
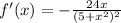
To find f'(2), simply substitute 2 into our derivative. So:
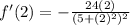
Multiply and square:
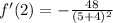
Add:
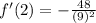
Square:
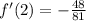
Reduce by 3:
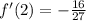
And we're done!