Answer:
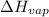 = 55.1 kJ/mol
= 55.1 kJ/mol
Explanation: Molar Enthalpy of Vaporization(
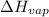 ) is the energy needed to change 1 mol of a substance from liquid to gas at constant temperature and pressure.
) is the energy needed to change 1 mol of a substance from liquid to gas at constant temperature and pressure.
For the 2-hydroxybiphenyl, there two temperatures and 2 pressures. In this case, use Clausius-Clapeyron equation:
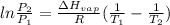
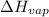 is in J/mol:
is in J/mol:
1) Temperature in K
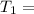 286 +273 = 559K
286 +273 = 559K
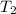 = 145 + 273 = 418K
= 145 + 273 = 418K
2) Both pressure in Pa
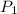 = 101325Pa
= 101325Pa
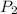 = 14*133 = 1862Pa
= 14*133 = 1862Pa
Since molar enthalpy is in Joules, gas constant R is 8.3145J/mol.K
Replacing into the equation:
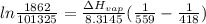
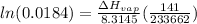
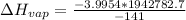
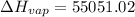
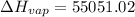
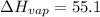 kJ/mol
kJ/mol
Using those values, molar enthalpy is 55.1 kJ/mol
Comparing to the CRC Handbook, which is
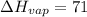 kJ/mol:
kJ/mol:
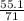 = 0.78
= 0.78
The calculated value is 0.78 times less than the CRC Handbook.