Answer:
*
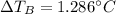
*
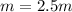
*
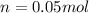
*
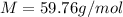
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, considering the boiling point rise problem, we consider its appropriate equation:

Whereas i is the van't Hoff factor that for this nonvolatile solute is 1, m is the molality, Kb the boiling point constant of water as it is the solvent and ΔT the temperature difference. In such a way, with the given information we obtain:
- ΔT:
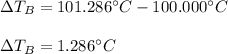
- Molality (mol/kg):
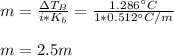
- Moles for 20.02 g (0.02002 kg) of water:
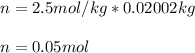
- Molar mass:
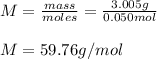
Best regards.