Answer:
(1)
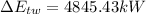
(2)
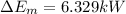
(3)
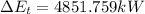
(4)
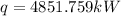
Step-by-step explanation:
At the saturation temperature, water starts boiling, and before that heat is added at constant pressure as latent heat.
From the saturated water-pressure table, at the pressure
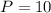 bar, we have
bar, we have
The saturated temperature of the water,
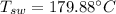
The specific volume of water,
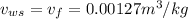
Specific enthalpy of water,
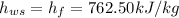
The given inlet temperature of the water,
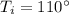 , so, latent heat added to the water to reach the saturation temperature is
, so, latent heat added to the water to reach the saturation temperature is
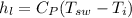
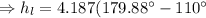
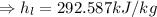
Now, specific enthalpy of the water at the inlet
 (specific enthalpy of the water at the saturation temperature)
(specific enthalpy of the water at the saturation temperature)
 (Latent heat capacity).
(Latent heat capacity).
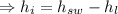
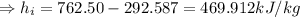
The specific volume of the water at intel is the same as the specific volume at the saturation temperature as volume remains unchanged on the addition of latent heat.
So,
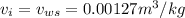 .
.
The outlet temperature,
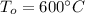 and pressure,
and pressure,
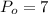 bar. From the superheated water table, we have
bar. From the superheated water table, we have
The specific volume of water,
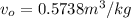
The specific enthalpy of water,
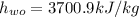
The given mass flow rate,
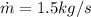 .
.
The inlet radius and outlet diameter are the same, i.e
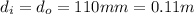 .
.
So, Inlet and outlet areas,
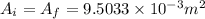 .
.
Let the inlet and outlet velocities be
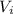 and
and
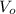 respectively.
respectively.
For the given specific volume,
 , and mass flow rate,
, and mass flow rate,
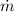 , the velocity,
, the velocity,
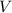 , at any cross-section having an area
, at any cross-section having an area
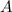 is
is
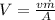 .
.
So, the inlet velocity,
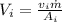
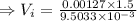
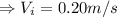 .
.
Similarly, the outlet velocity,
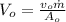
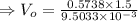
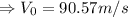 .
.
(1) The change in combined thermal energy and work flow
 Change in the thermal energy
Change in the thermal energy
 Change in the flow work
Change in the flow work
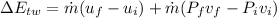
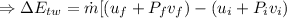
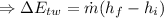
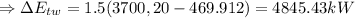
(2)The change in mechanical energy
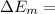 Change in kinetic energy + change in potential energy
Change in kinetic energy + change in potential energy
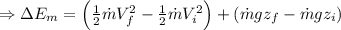
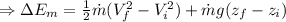
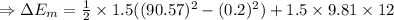
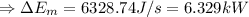
(3) The change in the total energy of water,
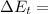 chnge in the thernal energy + change in the flow work + change in the mechanical energy
chnge in the thernal energy + change in the flow work + change in the mechanical energy
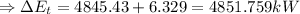 [from part (1) and (2)]
[from part (1) and (2)]
(4) Now, as there is no work done by the water, so, the heat input only caused the change in the total energy.
Hence, the rate of heat transfer,
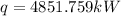 [from part (3).
[from part (3).