The functions g(x) and h(x) are transformations of the parent function f(x) = x^2 involving reflections, horizontal shifts (translations), and vertical shifts. g(x) reflects the parabola downwards and shifts it left and up, while h(x) shifts the parabola left and down.
Transformations of the Parent Function f(x) =
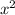
Let's consider two transformations of the parent function f(x) =
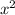 :
:
g(x) = -
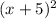 + 2 involves multiple transformations.
+ 2 involves multiple transformations.
The negative sign in front of the squared term reflects the parabola across the x-axis, which means it opens downwards.
The addition of 5 to the x before squaring results in a horizontal translation 5 units to the left.
Lastly, the addition of 2 at the end of the function translates the parabola vertically 2 units up.
h(x) =
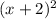 - 7 also includes a couple of transformations.
- 7 also includes a couple of transformations.
The positive squared term indicates that the parabola opens upwards, maintaining the orientation of the parent function.
Adding 2 to the x before squaring shifts the parabola horizontally 2 units to the left, and subtracting 7 from the function moves it vertically 7 units down.
These transformations alter the graph's position and orientation but not its fundamental shape, which remains a parabola.