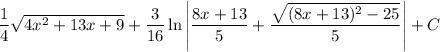Looks like the integral should be
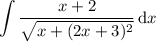
Expand the denominator:
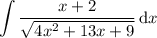
Notice that

In order to use this substitution, expand the integral as
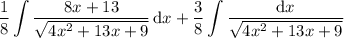
In the first integral, use the previously mentioned substitution:
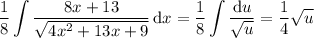
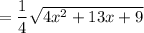
In the second integral, complete the square in the denominator:
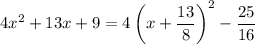
Now substitute
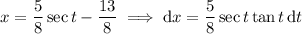
so that
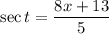
Then
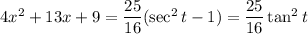
and the integral becomes
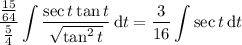
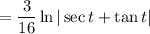
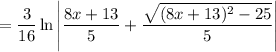
So, the integral is