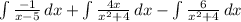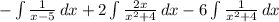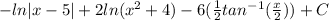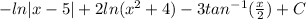Answer:
-ln|x−5| + 2 ln(x²+4) + 3 tan⁻¹(x/2) + C
Explanation:
The fraction will be split into a sum of two other fractions.
The first fraction will have a denominator of x − 5. The numerator will the a polynomial of one less order, in this case, a constant A.
The second fraction will have a denominator of x² + 4. The numerator will be Bx + C.
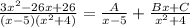
Combine the two fractions back into one using the common denominator.
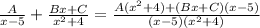
This numerator will equal the original numerator.
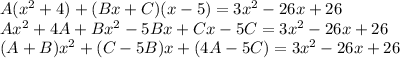
Match the coefficients.
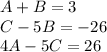
Solve the system of equations.
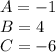
So we can rewrite the integral as:
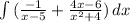
Solving: