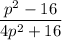Answer:
Explanation:
I will work with radians.
![$\frac {\cos^2 \left((\pi)/(2)-x \right)+\sin(-x)-\sin^2 \left((\pi)/(2)-x \right)+\cos \left((\pi)/(2)-x \right)} {[\sin(\pi -x)+\cos(-x)] \cdot [\sin(2\pi +x)\cos(2\pi-x)]}$](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/q69a5u5yl8mig3sma4sb1xsou847akr66f.png)
First, I will deal with the numerator
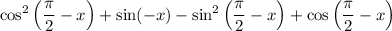
Consider the following trigonometric identities:
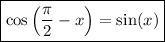
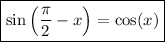
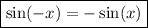
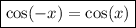
Therefore, the numerator will be
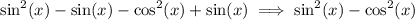
Once
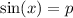
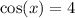
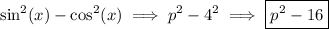
Now let's deal with the numerator
![[\sin(\pi -x)+\cos(-x)] \cdot [\sin(2\pi +x)\cos(2\pi-x)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/inieey7vh586wo4grx1jyz0z1mhcmcwe96.png)
Using the sum and difference identities:
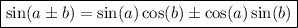
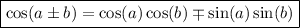
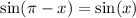
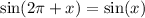
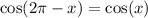
Therefore,
![[\sin(\pi -x)+\cos(-x)] \cdot [\sin(2\pi +x)\cos(2\pi-x)] \implies [\sin(x)+\cos(x)] \cdot [\sin(x)\cos(x)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/k014paxcv42wk57f6qh1oci1momyclaris.png)
![\implies [p+4] \cdot [p \cdot 4]=4p^2+16p](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/7yow6e6ztnkde4qcjis3kgvzxulibu30f0.png)
The final expression will be