Answer:
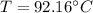
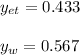
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, the Raoult's law for this problem is:
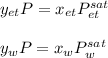
Which can be written as:
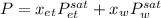
Thus, by using the Antoine equation, we can symbolically represent the the temperature at which such mixture boil:
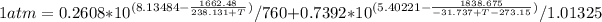
The solution, by numerical iteration process (there is not way to solve it analytically) is 92.16 °C considering the data extracted from NIST database. Next, vapor fractions are:
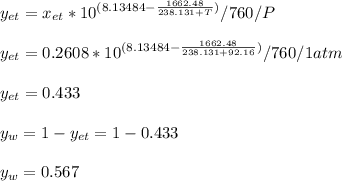
Regards.