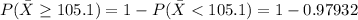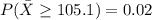Answer:
1
The correct option is C
2
The correct option is C
3
The correct option is A
4
The correct option is B
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The population mean is
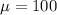
The standard deviation is
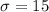
The sample size is

The sample mean is
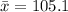
Generally
The null hypothesis is
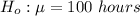
The alternative hypothesis is
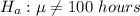
Given that the null hypothesis is true then the distribution of sample means
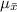 , from a sample size of 36 is mathematically represented as
, from a sample size of 36 is mathematically represented as
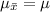
=>
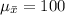
According to the Central Limit Theorem the test stated in the question is approximately normally distributed if the sample size is sufficiently large
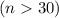 so given that the sample size is large n = 36
so given that the sample size is large n = 36
Then the test is normally distributed and hence the standard deviation is 15
Generally the standard error of mean is mathematically represented as
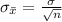
=>
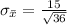
=>
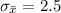
Generally the approximate probability of observing a sample mean of 105.1 or more is mathematically represented as
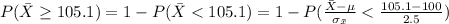
=>
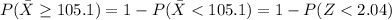
From the z-table (reference calculator dot net )
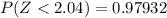
So