Answer:
Chloride (Cl⁻) and sodium (Na⁺) ions.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, since the aqueous species are actually dissociated when reacting and the solid species (ferric carbonate) remains undissolved, we can modify the given reaction as follows:
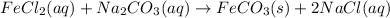
In such a way, dissociating the aqueous species we obtain:
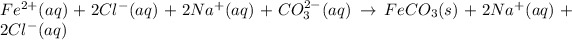
It means that the net ionic equation is:
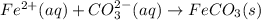
Therefore, the spectator ions are those were cancelled out, chloride (Cl⁻) and sodium (Na⁺).
Best regards.