Answer:
k > 8
Explanation:
Step 1: We know in order for a quadratic equation to have 2 distinct solutions the discriminant has to be positive
Important formula: Discriminant =
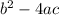
Step 2: Input information into discriminant
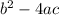 > 0
> 0
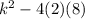 > 0
> 0
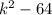 > 0
> 0
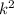 > 64
> 64
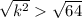
k > 8
Therefore in order for the equation to have 2 distinct solutions is to have k > 8