Find the critical points of
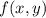 :
:
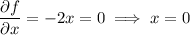
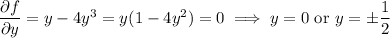
All three points lie within
 , and
, and
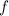 takes on values of
takes on values of
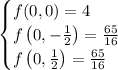
Now check for extrema on the boundary of
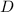 . Convert to polar coordinates:
. Convert to polar coordinates:
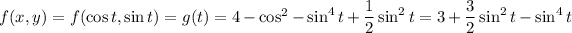
Find the critical points of
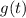 :
:
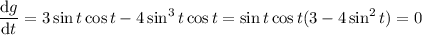
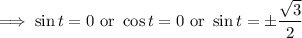
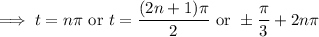
where
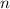 is any integer. There are some redundant critical points, so we'll just consider
is any integer. There are some redundant critical points, so we'll just consider
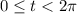 , which gives
, which gives
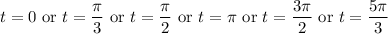
which gives values of
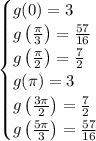
So altogether,
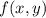 has an absolute maximum of 65/16 at the points (0, -1/2) and (0, 1/2), and an absolute minimum of 3 at (-1, 0).
has an absolute maximum of 65/16 at the points (0, -1/2) and (0, 1/2), and an absolute minimum of 3 at (-1, 0).