Answer:
The calculated value of z = - 0.197 falls in the critical region therefore we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that at the 5% significance level there is significant difference in population proportions of households that decorate their houses with lights for the holidays
Explanation:
We formulate the null and alternative hypotheses as
H0: p1= p2 there is no difference in population proportions of households that decorate their houses with lights for the holidays
against Ha : p1≠ p2 (claim) ( two sided)
The significance level is set at ∝= 0.05
The critical value for two tailed test at alpha=0.05 is ± 1.96
or Z∝= 0.05/2= ± 1.96
The test statistic is
Z = p1-p2/√pq(1/n1 +1/n2)
p1= proportions of households decorating in city 1 = 45/60=0.75
p2= proportions of households decorating in city 2 = 40/50= 0.8
p = the common proportion on the assumption that the two proportion are same.
p =
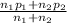
Calculating
p =60 (0.75) + 50 (0.8) / 110
p= 45+ 40/110= 85/110 = 0.772
so q = 1-p= 1- 0.772= 0.227
Putting the values in the test statistic and calculating
z= 0.75- 0.8/ √0.772*0.227( 1/60 + 1/50)
z= -0.05/√ 0.175244 ( 110/300)
z= -0.05/0.25348
z= -0.197
The calculated value of z = - 0.197 falls in the critical region therefore we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that at the 5% significance level there is significant difference in population proportions of households that decorate their houses with lights for the holidays