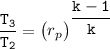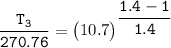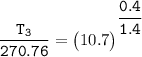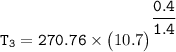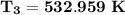Answer:
a. the temperature (K) at state 2 is
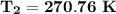
b. the pressure (kPa) at state 2 is
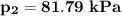
c. the specific enthalpy (kJ/kg) at state 2 is
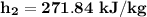
d. the temperature (K) at state 3 is
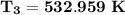
Step-by-step explanation:
From the given information:
T1 (K) = 249
P1 (kPa) = 61
V1 (m/s) = 209
rp = 10.7
rc = 1.8
The objective is to determine the following:
a. Determine the temperature (K) at state 2.
b. Determine the pressure (kPa) at state 2.
c. Determine the specific enthalpy (kJ/kg) at state 2.
d. Determine the temperature (K) at state 3.
To start with the specific enthalpy (kJ/kg) at state 2.
By the relation of steady -flow energy balance equation for diffuser (isentropic)
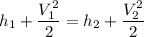
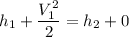
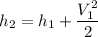
For ideal gas;enthalpy is only a function of temperature, hence
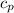 T = h
T = h
where;
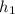 is the specific enthalpy at inlet =
is the specific enthalpy at inlet =
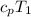
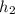 is the specific enthalpy at outlet =
is the specific enthalpy at outlet =
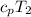
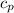 = 1.004 kJ/kg.K or 1004 J/kg.K
= 1.004 kJ/kg.K or 1004 J/kg.K
Given that:
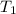 (K) = 249
(K) = 249
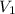 (m/s) = 209
(m/s) = 209
∴
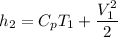
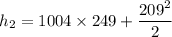
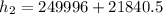
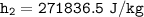
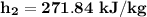
Determine the temperature (K) at state 2.
SInce;
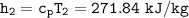
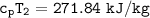
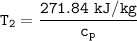
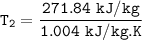
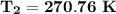
Determine the pressure (kPa) at state 2.
For isentropic condition,
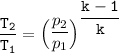
where ;
k = specific heat ratio = 1.4
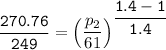
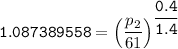
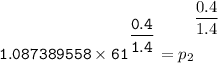
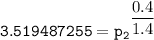
![\mathtt{ \mathbf{ p_2 = \sqrt[0.4]{3.519487255^(1.4)} }}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/p6flayjxzlkq9qcubncsnx5ix1f4bakqdm.png)
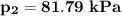
d. Determine the temperature (K) at state 3.
For the isentropic process
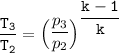
where;
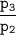 is the compressor ratio
is the compressor ratio
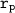
Given that ; the compressor ratio
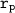 = 10.7
= 10.7