Answer: Speed =
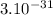 m/s
m/s
Step-by-step explanation: Like in classical physics, when external net force is zero, relativistic momentum is conserved, i.e.:
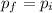
Relativistic momentum is calculated as:
p =
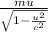
where:
m is rest mass
u is velocity relative to an observer
c is light speed, which is constant (c=
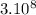 m/s)
m/s)
Initial momentum is zero, then:
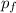 = 0
= 0
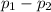 = 0
= 0
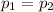
To find speed of the heavier fragment:
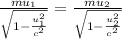
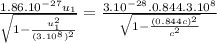
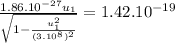
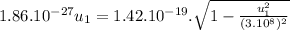
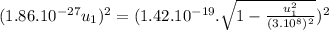
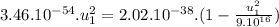
![3.46.10^(-54).u_(1)^(2) = 2.02.10^(-38) -[2.02.10^(-38)((u_(1)^(2))/(9.10^(16)) )]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/6cvm34b355oi31i3aw8xj6c53qb0mwqglk.png)
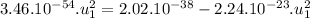
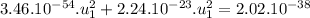
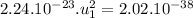
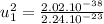
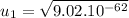
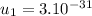
The speed of the heavier fragment is
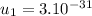 m/s.
m/s.