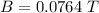Answer:
The magnetic field is
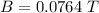
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The mass of the metal is
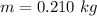
The current is
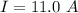
The distance between the rail(length of the rod ) is
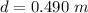
The coefficient of kinetic friction is
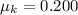
Generally the magnetic force is mathematically represented as
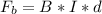
Given that the rod is moving at a constant velocity, it
=>
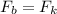
Where
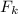 is the kinetic frictional force which is mathematically represented as
is the kinetic frictional force which is mathematically represented as
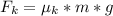
So
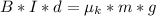
=>
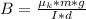
substituting values
=>
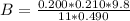
=>