Answer: The vapor pressure of water at 10°C will be less as compared with its vapor pressure at 50°C.
Step-by-step explanation:
Vapor pressure of a liquid is defined as the pressure exerted by the vapors in equilibrium with the liquid/solution at a particular temperature.
As Kinetic energy is dependent on the absolute temperature of the gas.
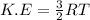
where R = gas constant
T = temperature
On increase in temperature, the kinetic energy of the molecules increase and thus more liquid molecules can escape to form vapours and thus will exert more vapor pressure.
Thus the vapor pressure of water at 10°C will be less as compared with its vapor pressure at 50°C.