Answer:
3-methylenehexane
Step-by-step explanation:
In this case, we have two clues.
1) The hydrogenation reaction
2) The ozonolysis reaction
See figure 1.
With this in mind, lets analyze each clue. In the first reaction, we know that only 1 molecule of
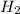 is added to the unknown molecule. This indicates that we only have 1 double bond in the molecule. Now, the next question is where is placed the double bond?
is added to the unknown molecule. This indicates that we only have 1 double bond in the molecule. Now, the next question is where is placed the double bond?
To answer this question, we have to use the second clue. In the ozonolysis reaction, a double bond is broken and is replaced with a carbonyl group. If, formaldehyde is formed the double bond is formed with a primary carbon. The primary carbons in the structure (given in the first reaction: 3-methylhexane) are carbons 1, 6, and 7. So, the double bond can be placed between carbons:
a) 6 and 5
b) 7 and 3
c) 1 and 2
To decide which one is the position of the double bond we have to keep in mind the second product of the ozonolysis reaction a ketone. With this in mind, the carbon bonded to the primary one (deduced by the formaldehyde) it has to be a tertiary carbon. The only option that has a primary carbon bonded to tertiary carbon is b). (See figure 2)
Finally, with this in mind the structure is 3-methylenehexane. To be sure, we can check the formula for the compound,
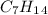 and the reactions. (See figure 3)
and the reactions. (See figure 3)
I hope it helps!