Answer:
critical clearing angle = 70.3°
Step-by-step explanation:
Generator operating at = 50 Hz
power delivered = 1 pu
power transferable when there is a fault = 0.5 pu
power transferable before there is a fault = 2.0 pu
power transferable after fault clearance = 1.5 pu
using equal area criterion to determine the critical clearing angle
Attached is the power angle curve diagram and the remaining part of the solution.
The power angle curve is given as
= Pmax sinβ
therefore : 2sinβo = Pm
2sinβo = 1
sinβo = 0.5 pu
βo =
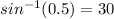 ⁰
⁰
also ; 1.5sinβ1 = 1
sinβ1 = 1/1.5
β1 =
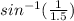 = 41.81⁰
= 41.81⁰
∴ βmax = 180 - 41.81 = 138.19⁰
attached is the remaining solution
The critical clearing angle =
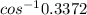 ≈ 70.3⁰
≈ 70.3⁰