Answer:
0.03 Joules have been converted into other forms of energy as the direct result of the collision.
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's start studying the conservation of momentum for the system:
![P_i=P_f\\(0.25\,kg)\,{0.6\,m/s)+(0.5\,kg)\,(0\,m/s)=(0.25\,kg+0.5\,kg)\, v_f \\\\\\ 0.15\,kg\,m/s=0.75\,kg\,\,v_f\\v_f=0.15/0.75\,\,m/s\\v_f=0.2\,\,m/s]()
Now that we know the speed of the newly created object, we can calculate how the final kinetic energy differs from the initial one:
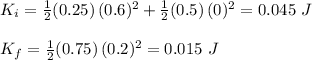
Then, when we subtract one from the other, we can estimate how much kinetic energy has been converted into other forms of energy in the collision:
0.045 J - 0.015 J = 0.03 J