Answer:
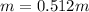
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, we can consider the n-propanol as the solute (lower amount) and the t-butanol as the solvent (higher amount), for which, initially, we must compute the moles of n-propanol (molar mass = 60.1 g/mol) as shown below:
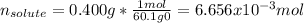
Since the molality is computed via:
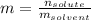
Whereas the mass of the solvent is used in kilograms (0.0130g for the given one). Thus, we compute the resulting molality of the solution:
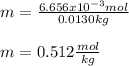
Or just:
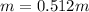
Best regards.