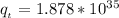Answer:
The value of the function is
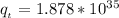
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The temperature is
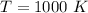
The volume is
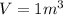
Generally the transnational partition function is mathematically represented as
![q__(t )} = [(2 * \pi * m * k * T )/( N_a * h) ]^{(3)/(2) } * V](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/9tjnc6g82jolx48jmcs306xaxbrcpkdpsi.png)
Where m is the molar mass of oxygen with a constant value of
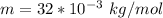
k is the Boltzmann constant with a value of
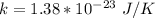
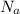 is the Avogadro Number with a constant value of
is the Avogadro Number with a constant value of

h is the Planck's constant with value
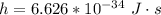
Substituting values
![q__(t )} = [(2 * 3.142 * 32*10^(-3) * 1.38 *10^(-23) * 1000 )/( 6.022 *10^(23) * [6.626 *10^(-34)] ^2 )]^{(3)/(2) } * 1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/gd2wivhff8cio99pycyysd4go9fmwyp21k.png)