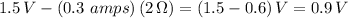Answer:
1. Current in the circuit; 1.2 Amps
See attached image for the circuit.
2. Equivalent resistor = 3 Ω
I = 0.3 amps
Potential difference across the battery terminals is: 0.9 V
Step-by-step explanation:
Part 1.
The internal resistance of 2 ohms is simply added to the circuit in series as shown in the attached image.
Since now we have two resistances in series (2 ohms and 3 ohms) the total of this series combination is 5 ohms. Using Ohm's law, we can derive the current running through the circuit:
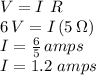
Part 2.
Now we have a 1.5 V battery with a 2 ohm internal resistance, connected to two identical 6 ohm resistors.
a. The equivalent resistance presented by the two resistors in parallel:
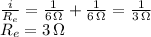
b. Now the circuit can be represented by a 2 ohm resistor (internal battery resistance) plus a 3 ohm parallel equivalent resistor in series. That is a 5 ohm total resistance. Then Ohm's law becomes:
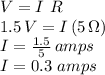
c. The potential difference across the battery terminals must be the battery's EMF minus the potential drop in its internal resistance: