Answer:
Q = 0.042 ft^3/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Given data
pressure drop = 1 psi ( p1 -p2) =
Gasoline density = 1.32 slugs/ft^3
viscosity = 3.26 8 10^-3 Ibf.s/ft^2
correct viscosity of gasoline = 6.5 *10^-6 Ibf.s/ft^2
e = 0.0004 ft
assumptions
Since The base is of constant diameter then V1 = V2
also z1 = z2
therefore the steady flow energy equation will be
hf = pressure drop / ( gasoline density * g ) ------ equation 1
hf = head loss due to friction
g = 32.174 ft/s^2
equation 1 becomes
note : 1 ibf = slug ft / s^2
hf =
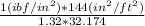 = 3.4 ft
= 3.4 ft
Volume flow rate can be obtained through iteration process using (hf)
therefore hf can be expressed as
hf = f * l/d * v^2/2g
fv^2 = hf * d/l * 2g ------------- equation 2
d = 1/12 (ft)
l = 10 (ft )
g = 32 .174 ft/s^2
insert the following values into equation 2
fv^2 = 1.823 (ft^2/s^2) -------------- equation 3
assuming full turbulent flow
e/d = 0.0004 / (1/12) = 0.0048 ft and
assuming Reynolds number ( re ) = 10^8
therefore from Moody's chart ; f = 0.03
insert ; f = 0.03 into equation 3
v =
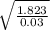 = 7.8 ft/s
= 7.8 ft/s
Now we have V = 7.8 ft/s then we have to calculate for Reynolds number
Re = Pvd / u
u = viscosity of gasoline
Re = 1.32 * 7.8 * (1/12) / (6.5 *10^-6)
Re = 1.32 * 10^5
hence at this Reynolds number the value of ; f = 0.031 as gotten when we assumed the Reynolds number
v =
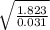 = 7.67 ft/s
= 7.67 ft/s
therefore the Volumetric flow rate
= Q =
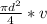
Q =
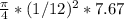 = 0.042 ft^3/s
= 0.042 ft^3/s