Answer:
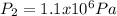
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello.
In this case, we can solve this problem by applying the Boyle's law which allows us to understand the pressure-volume behavior as a directly proportional relationship:
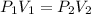
In such away, knowing the both the initial pressure and volume and the final volume, we can compute the final pressure as shown below:
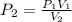
Consider that the given initial pressure is also equal to Pa:
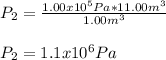
Which stands for a pressure increase when volume decreases.
Regards.