Answer:
Nitrogen = 0.3 atm
Oxygen = 0.25 atm
Argon = 0.45 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
According to Dalton's law of partial pressure, the total pressure in the container is equal to sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases.
Given;
Total pressure of the gases, P_total = 1 atm
Pressure of nitrogen, P_nitrogen = 0.3 atm
Pressure of oxygen, P_oxygen = 0.25 atm
Pressure of argon, P_argon = ?
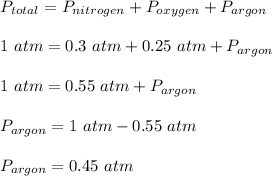
Therefore, the contribution of each gas to the total pressure of the gas mixture is;
Nitrogen = 0.3 atm
Oxygen = 0.25 atm
Argon = 0.45 atm