Answer:
Reagents: 1)
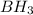 2)
2)
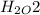 ,
,
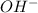
Mechanism: Hydroboration
Step-by-step explanation:
In this case, we have a hydration of alkenes reaction. But, in this example, we have an anti-Markovnikov reaction. In other words, the "OH" is added in the least substituted carbon. Therefore we have to choose an anti-Markovnikov reaction: "hydroboration".
The first step of this reaction is the addition of borane (
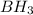 ) to the double bond. Then in the second step, we have the deprotonation of the hydrogen peroxide, to obtain the peroxide anion. In the third step, the peroxide anion attacks the molecule produced in the first step to produce a complex compound in which we have a bond "
) to the double bond. Then in the second step, we have the deprotonation of the hydrogen peroxide, to obtain the peroxide anion. In the third step, the peroxide anion attacks the molecule produced in the first step to produce a complex compound in which we have a bond "
 ". In step number 4 we have the migration of the C-B bond to oxygen. Then in step number 5, we have the attack of
". In step number 4 we have the migration of the C-B bond to oxygen. Then in step number 5, we have the attack of
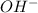 on the
on the
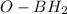 to produce an alkoxide. Finally, the water molecule produce in step 2 will protonate the molecule to produce the alcohol.
to produce an alkoxide. Finally, the water molecule produce in step 2 will protonate the molecule to produce the alcohol.
See figure 1
I hope it helps!