Answer:
g(x)<j(x)<k(x)<f(x)<m(x)<h(x)
Explanation:
1.
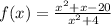
The denominator of f is defined for all real values of x
Therefore, the function is continuous on the set of real numbers
3.
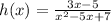
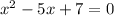
It cannot be factorize .
Therefore, it has no real values for which it is not defined .
Hence, function h is defined for all real values.
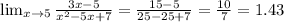
2.
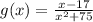
The denominator of g is defined for all real values of x.
Therefore, the function g is continuous on the set of real numbers
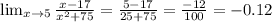
4.
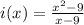
x-9=0
x=9
The function i is not defined for x=9
Therefore, the function i is not continuous on the set of real numbers.
5.
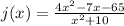
The denominator of j is defined for all real values of x.
Therefore, the function j is continuous on the set of real numbers.
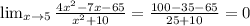
6.
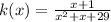

It cannot be factorize .
Therefore, it has no real values for which it is not defined .
Hence, function k is defined for all real values.
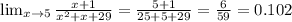
7.
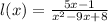
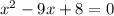
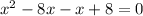
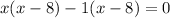
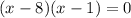
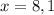
The function is not defined for x=8 and x=1
Hence, function l is not defined for all real values.
8.
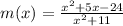
The denominator of m is defined for all real values of x.
Therefore, the function m is continuous on the set of real numbers.
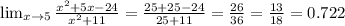
g(x)<j(x)<k(x)<f(x)<m(x)<h(x)