Answer:
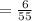
Explanation:
The computation of experimental probability is shown below:-
The Number of king in a well shuffled deck consists 52 cards which is
= 4
The Number of ways of drawing consists of 4 king in 13 repetitions which is
=
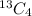
In 13 repetition, 2 kings are drawn by
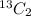 way
way
Now,
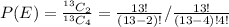
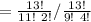
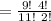
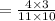
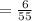
Therefore for computing the experimental probability we simply applied the above formula.