Answer: D. 430 K
Step-by-step explanation:
Using Gibbs Helmholtz equation:
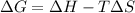
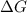 = Gibbs free energy
= Gibbs free energy
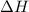 = enthalpy change = 62.4 kJ/mol
= enthalpy change = 62.4 kJ/mol
![\Delta S = entropy change = 0.145 kJ/mol K</p><p>T = temperature in Kelvin</p><p>[tex]\Delta G](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/ky9a7iifl2jy2wuk6q0xibaanpzdb30bsd.png) = +ve, reaction is non spontaneous
= +ve, reaction is non spontaneous
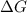 = -ve, reaction is spontaneous
= -ve, reaction is spontaneous
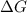 = 0, reaction is in equilibrium
= 0, reaction is in equilibrium
At equilibrium :
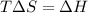
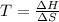
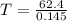
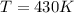
Thus at 430 K , the reaction is at equilibrium.