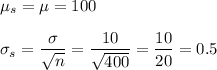Answer:
a. Mean = 100, S.D. = 3.333
b. Mean = 100, S.D. = 2.582
c. Mean = 100, S.D. = 1.667
d. Mean = 100, S.D. = 1.414
e. Mean = 100, S.D. = 1
f. Mean = 100, S.D. = 0.5
Explanation:
The question is incomplete:
Population mean: 100
Population standard deviation: 10.
The mean for any sampling distribution is equal to the population mean.
The standard deviation for the sampling distribution depends on the population standard deviation and the sample size as:
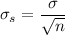
We can calculate the parameters of the sampling distributions as:
a. n = 9
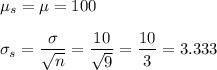
b. n = 15
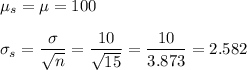
c. n = 36
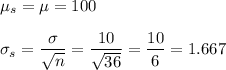
d. n = 50
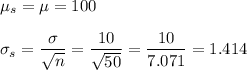
e. n = 100
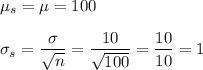
f. n = 400