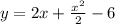Answer:
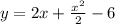
Explanation:
Solution:-
- We are given the following initial value problem:
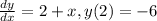
- We will first isolate the variables:
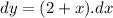
- Perform integration for both sides of the equation:
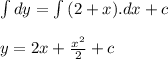
Where,
c: The constant of integration
- We will solve for the constant of integration by using the initial value y ( 0 ) = -6 as follows:
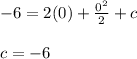
- The final solution can be expressed as follows: