Answer:
A)
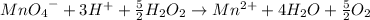
B) 7.5 molar
Step-by-step explanation:
A) Reduction
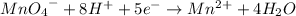
Oxidation
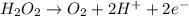
Multiplying the oxidation reaction by 5/2 and adding it to the reduction equation:
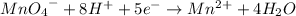
+
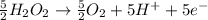
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
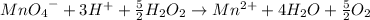
B) 10 ml = 0.01 L
20 ml = 0.02 L
mol of MnO4− = molarity*volume = 1.5*0.02 = 0.03
1 mol of MnO4− reacts with 5/2 mol of H2O2, then:
mol of H2O2 = 0.03*5/2 = 0.075
molarity = mol/volume = 0.075/0.01 = 7.5 molar