Answer:
![P(X\geq 2)=1- P(X<2)= 1-[P(X=0) +P(X=1)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/dya2u9slo39oxjkocqhm3ardf9wcm939k4.png)
And using the probability mass function we can find the individual probabilities:
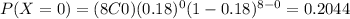
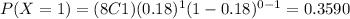
And replacing we got:
![P(X\geq 2)=1 -[0.2044 +0.3590]= 0.4366](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/q24exehqr9jt30q2frhb097ofl7jp41yj5.png)
Then the probability that at least 2 disapprove of daily pot smoking is 0.4366
Explanation:
Let X the random variable of interest "number of seniors who disapprove of daily smoking ", on this case we now that:
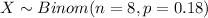
The probability mass function for the Binomial distribution is given as:
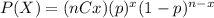
Where (nCx) means combinatory and it's given by this formula:
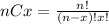
And we want to find this probability:
![P(X\geq 2)=1- P(X<2)= 1-[P(X=0) +P(X=1)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/dya2u9slo39oxjkocqhm3ardf9wcm939k4.png)
And using the probability mass function we can find the individual probabilities:
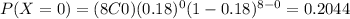
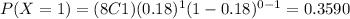
And replacing we got:
![P(X\geq 2)=1 -[0.2044 +0.3590]= 0.4366](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/q24exehqr9jt30q2frhb097ofl7jp41yj5.png)
Then the probability that at least 2 disapprove of daily pot smoking is 0.4366