Answer:
A score of 1920 has a z-score of 1.27.
A score of 1290 has a z-score of -0.74.
A score of 2220 has a z-score of 2.23.
A score of 1420 has a z-score of -0.32.
The score of 2220 is more than two standard deviations from the mean, so it is unusual.
Explanation:
When the distribution is normal, we use the z-score formula.
In a set with mean
 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
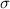 , the zscore of a measure X is given by:
, the zscore of a measure X is given by:
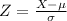
The Z-score measures how many standard deviations the measure is from the mean. After finding the Z-score, we look at the z-score table and find the p-value associated with this z-score. This p-value is the probability that the value of the measure is smaller than X, that is, the percentile of X. Subtracting 1 by the pvalue, we get the probability that the value of the measure is greater than X.
If X is 2 or more standard deviations from the mean, it is considered unusual.
In this question, we have that:
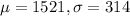
Score of 1920:
X = 1920. Then
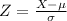
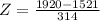
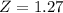
A score of 1920 has a z-score of 1.27.
Score of 1290:
X = 1290. Then
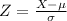
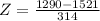

A score of 1290 has a z-score of -0.74.
Score of 2220:
X = 1290. Then
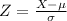
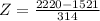
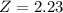
A score of 2220 has a z-score of 2.23.
Since it is more than 2 standard deviations of the mean, the score of 2220 is unusual.
Score of 1420:
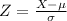
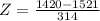

A score of 1420 has a z-score of -0.32.